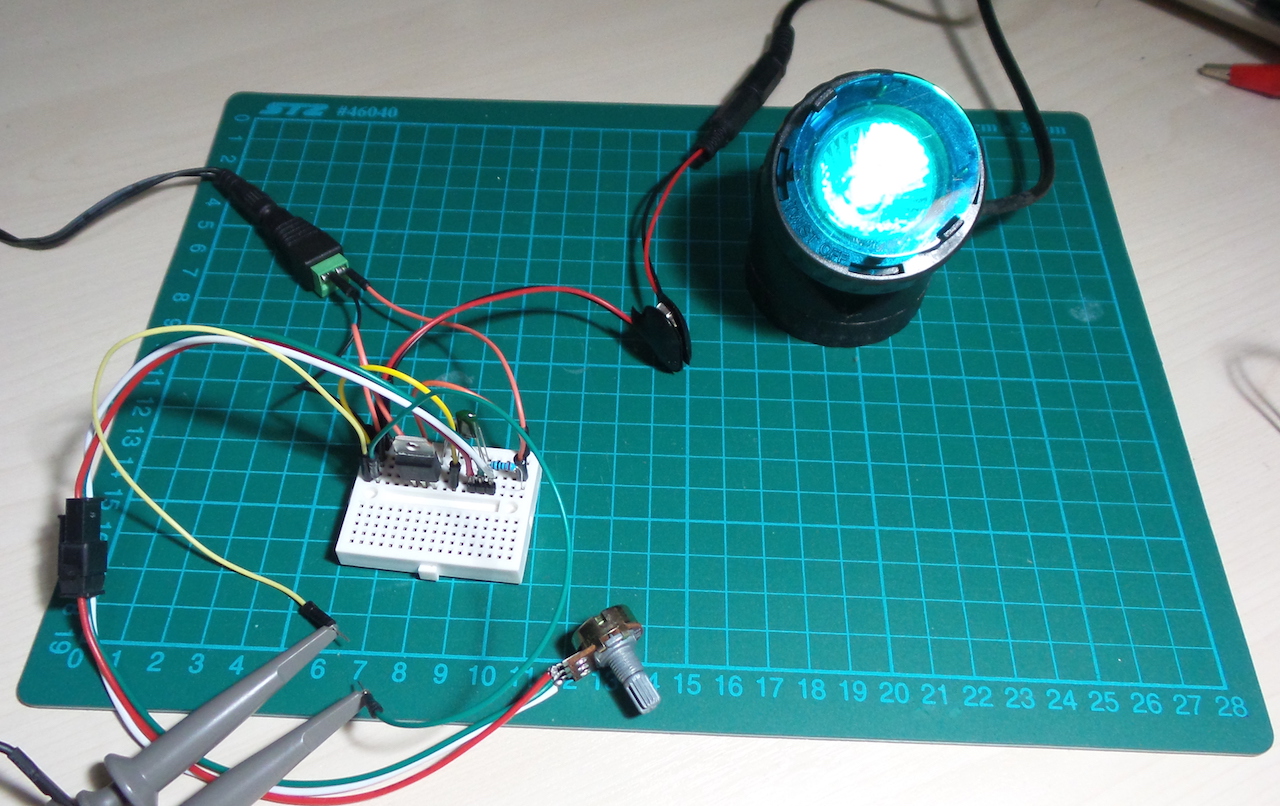
LEAP#205 Triac Dimmer
A triac is a "bidirectional thyristor" because it conducts in both directions and is typically used in AC
applications.
The basic behaviour of a triac can be summarised in two rules:
- Rule 1. To turn ON, a gate current ≥ IGT must be applied until the load current is ≥ IL (latching current).
- Rule 2. To turn OFF (commutate), the load current must be < IH (holding current) for long enough for the device to return to the blocking state.
-
read more and comment..
LittleArduinoProjects now with fancy catalog!
I keep finding new uses for GitHub Pages - situations where in the past I would otherwise have spun up a web site on
heroku or similar. But if the site can be static, and especially if you are already hosting the git repository at
GitHub, Pages are perfect.
For a long time, I've maintained the LittleArduinoProjects project index as a simple table in the README. But it wasn't
particularly nice or usable, so I decided to pimp it up and serve the catalog index with pages. Turned out to be a
piece of cake (with a few scripts to convert the old index to JSON for the catalog page.
So here it is, Little Electronics & Arduino Projects at
leap.tardate.com:
As always - and since the gh-pages code lives in the same repo - all notes and code for the catalog are available in the same Little Electronics & Arduino Projects repo on GitHub.
read more and comment..
On "random" CI failures
I closed a bug yesterday that's been kicking around for almost a year as a sometimes fails on CI but no-one can
figure out why frustration.
Sooner or later you'll hear someone suspect it must be a problem with CI. Which is ironically funny in a
shoot-the-messenger kind of way!
Thankfully our "CI issue" turned into a for-real bug. In short, the code involved many classes with near 100% test
coverage. It had been read and re-read and everyone would swear there's no way this could fail.
No, of course we were wrong. The bug was basically a conspiracy of two bits of code in two very different places:
- a record validation that ensured field1 was not the same as field2
- a data collection routine that could be configured to filter/replace sensitive values with a random ** string: ["*" * rand(4..10)]
And you can see where this leads: our problem was filtered data ending up by obscure and circuitous means in field1 and field2 ... with a 1 in 7 chance of the record validation failing (never happens on our machines of course). After that it was an easy fix.
So once again we learn the lesson:
If CI say red but we can't figure out why, "must be a problem with CI" is 99.999% the wrong answer. It just means we haven't found the bug yet.
I've seen this scenario play out a dozen times in as many years, and CI was always right;-) Since it keeps cropping up, it made me think about how to best knock these on the head. Five things:
start by assuming there is a bug until proven otherwise
It's too easy to give up, find scape-goats or "magic" explanations otherwise.
Take heart in the fact that if you assume CI is right, the odds are on your side.
put a canary in a coalmine
When we first encountered this issue and failed to find the root cause, we added code to catch the "this is about to fail in that unexpected way" situation and log/report appropriately.
So while the ticket got iced, it's been that "canary" that keeps dying in order to keep the issue alive! So when it died again yesterday, it was a painful reminder to get to the bottom of the issue once and for all.
finding bugs .. is like looking for your keys
Always found in the last place to look. So when you've honed in on the code you think is failing, studied it upside down, left to right, and still can't find the issue .. maybe it's time to consider you might be right. Throw out that hypothesis, pull back and fan out instead.
treat random errors like a lottery
If errors happen infrequently, reproducing them is like trying to win the lottery. The more entries, the better your chances.
So don't run tests a few times, run them millions of times if you have to. Computers are good at this. That's how I diagnosed this latest issue while tweaking logging and the test itself. Bash away:
for (( ; ; )) ; do
rspec spec/that_wierd_spec.rb
if [ $? == 1 ]
then
echo "JACKPOT!"
break
fi
done
random failures ... might really be random
This sounds so simple that it's easy to overlook.
If things fail randomly .. it only takes a few moments to search the code to see if anything is using something similar to a random function.
Could it be possible that random failures and the use of rand() might be related?!
May be not, but if they are, that's a cheap win!
read more and comment..
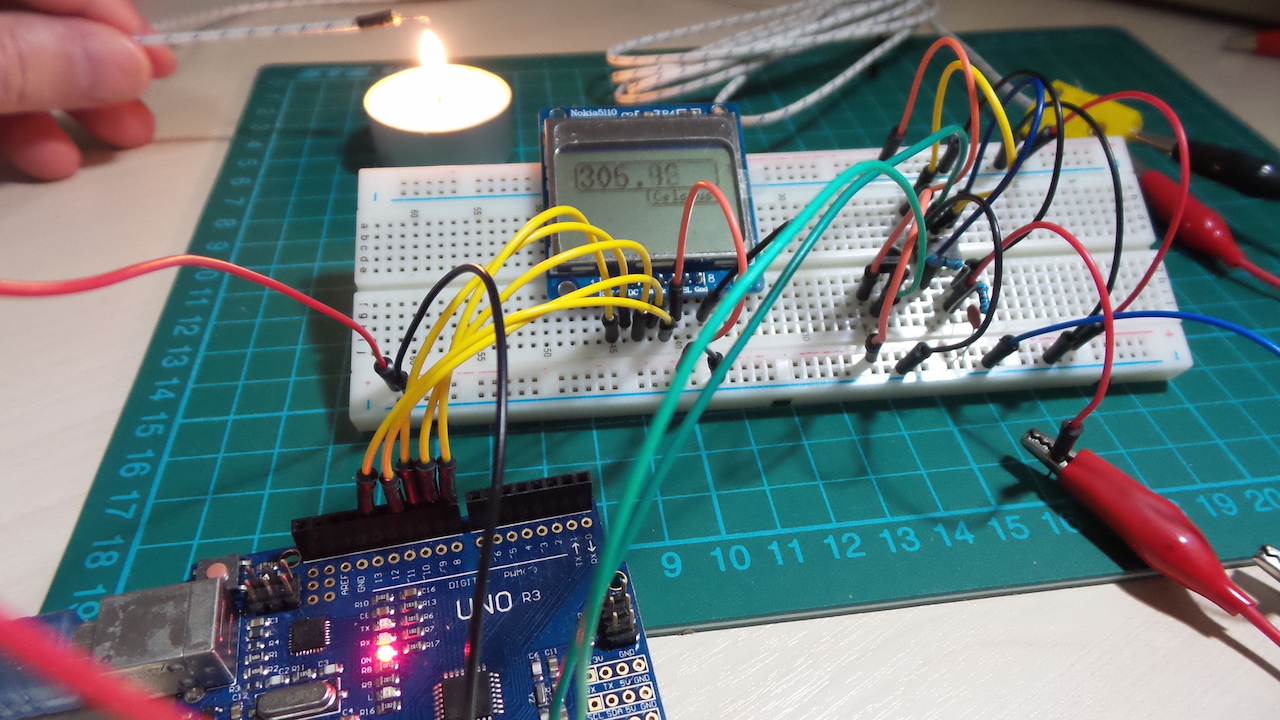
LEAP#204 Type K Temperature Logger
I'm working on an idea where I need to measure temperatures to around 500°C - above those typically supported with
semiconductor sensors or thermistors.
This project demonstrates the basic approach using an Arduino as the "temperature logger". I'm using a K Type
thermocouple that's rated up to 700°C. Since thermocouples only measure a differential temperature, I'm also using an
LM35 to provide the cold-junction baseline. The temperature measurement is displayed on a 5110 LCD.
As always, all
notes, schematics and code are in the Little Electronics & Arduino Projects repo on GitHub.
read more and comment..